In the realm of property maintenance and indoor air quality, issues like mold growth are persistent and concerning. This unwelcome intruder not only damages structures but also poses significant health risks to occupants.
As the battle against mold continues, innovative techniques emerge, promising more efficient and thorough solutions. Among these, fogging has garnered attention as a potentially game-changing method in mold remediation. But how effective is fogging for mold remediation?
Its ability to reach areas inaccessible to traditional cleaning methods makes it an intriguing option in the mold remediation toolkit. However, as with any emerging technique, questions arise about its true efficacy and appropriate applications.
This article delves into the world of mold remediation fogging, exploring its principles, potential benefits, and limitations. We’ll examine the science behind this method and consider its place in the broader context of mold control strategies.

How Effective Is Fogging for Mold Remediation
Fogging is a mold remediation technique that disperses a fine mist of antimicrobial solution throughout affected areas, reaching into cracks and crevices. It uses specialized equipment to create a fog-like substance containing biocides or mold-killing agents. With this in mind, does mold fogging work?
While fogging offers advantages like extensive coverage and time efficiency, it also has limitations. It primarily treats surface mold and may not penetrate deeply into porous materials.
Fogging should be used as part of a comprehensive remediation plan, not as a standalone solution. It’s most effective when combined with addressing moisture issues and physically removing mold-infested materials.
Overall, fogging can be a useful tool in mold remediation, but its effectiveness depends on proper application and integration with other remediation strategies.
The Fogging Process
Preparation for fogging
Pre-fogging inspection and assessment
A thorough inspection is crucial before initiating the fogging process. This step involves carefully examining the area to identify the extent of mold growth and assess moisture levels.
Experts evaluate whether fogging is the most appropriate treatment method. They consider factors such as the type of mold, surface materials, and the overall scope of the infestation.
Preparing the area for fogging
Proper preparation involves sealing off the treatment area to prevent the fog from escaping. This typically includes covering vents, closing windows, and sealing doorways with plastic sheeting.
All personal items, furniture, and sensitive equipment should be removed or covered. The space must be cleared to ensure maximum coverage and effectiveness of the fogging treatment.
Execution of fogging
Fogging equipment and chemicals
Fogging typically utilizes ultra low volume (ULV) foggers, which produce a fine mist capable of reaching small crevices. These devices are designed for efficient and uniform distribution of the treatment solution.
The chemicals used in fogging are usually biocides or antimicrobials specifically formulated to combat mold. These solutions are chosen based on their effectiveness against specific mold types and safety for use in indoor environments.
Application of the fogging treatment
The fogging process begins with the activation of the ULV fogger, dispersing the antimicrobial solution throughout the space. The duration varies depending on the room size and infestation severity.
Technicians ensure complete coverage by moving systematically through the area. They wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) to safeguard against chemical exposure during the application.
Post-fogging procedures
Ventilation and drying
After fogging, proper ventilation is essential to allow the chemicals to dissipate and surfaces to dry. This typically involves opening windows and using fans to circulate air.
The drying process helps prevent moisture accumulation, which could lead to new mold growth. The duration of this phase depends on factors like humidity levels and air circulation.
Follow-up inspection and testing
Post-treatment inspection involves visually checking treated areas for any remaining signs of mold. This helps ensure the effectiveness of the fogging process.
Air quality testing is often conducted to measure mold spore levels and confirm successful remediation. If necessary, additional treatments or adjustments to the remediation plan may be recommended.
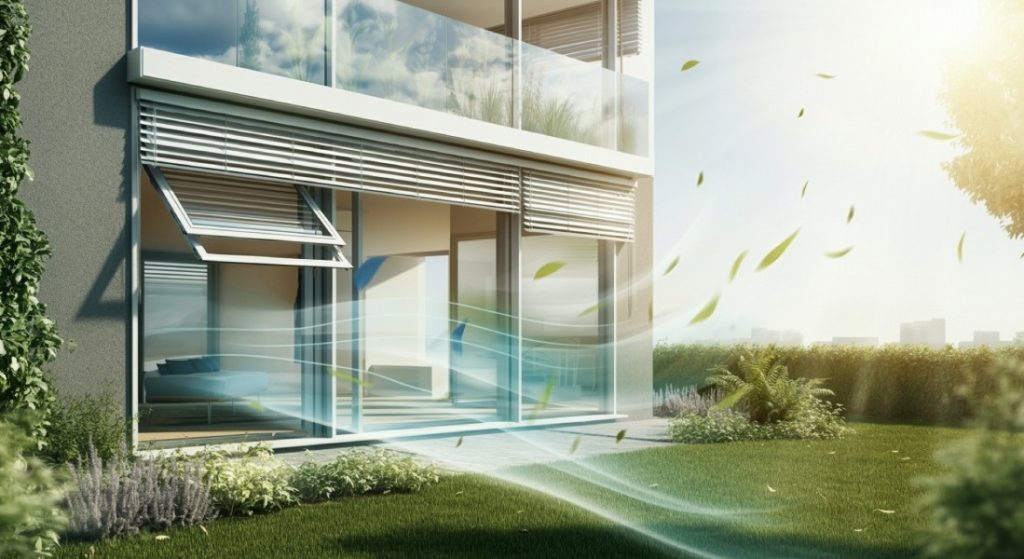

Benefits of Fogging for Mold Remediation
Fogging for mold remediation offers extensive coverage, penetrating hard-to-reach areas and treating large spaces efficiently. It provides comprehensive disinfection by eliminating mold spores on surfaces and in the air. The method is time-efficient, allowing for rapid application and shorter overall remediation time.
The fine mist can seep into wall cavities, crawl spaces, and other concealed areas, ensuring thorough treatment of structural elements. This efficiency translates to cost savings, reduced disruption for occupants, and quicker return to normal use of the treated space.
While fogging offers numerous benefits, it’s crucial to remember that it should be part of a comprehensive mold remediation strategy. When used in conjunction with other methods, fogging can significantly enhance the overall effectiveness of mold treatment and prevention efforts.
Comparing Fogging to Other Mold Remediation Methods
Comparing fogging to other mold remediation methods reveals distinct advantages and limitations. Traditional physical removal ensures thorough elimination of visible mold but can be labor-intensive and disruptive.
Comprehensive remediation addresses root causes through inspection, containment, and moisture control. It offers long-term solutions. However, this approach requires more time and resources.
Fogging, while effective for reaching hidden areas and treating large spaces quickly, is often most beneficial when used as a supplementary treatment. It excels in scenarios where minimal disruption is crucial or as a final step in remediation.
The ideal approach often combines methods, with fogging complementing physical removal and comprehensive strategies.
Choosing the Right Professionals
When selecting mold remediation experts, especially for fogging treatments, prioritize certified specialists. Look for certifications from recognized organizations like IICRC or NORMI. These credentials indicate high expertise and adherence to industry standards.
Certified professionals are trained in mold remediation techniques, including safe fogging applications. They understand safety protocols, risk assessment, and proper chemical handling. Their expertise covers establishing containment areas and using appropriate protective equipment.
Hiring certified specialists ensures effective and safe mold remediation. This choice guarantees compliance with industry best practices. It protects both occupants and the remediation team throughout the process.

Conclusion
In conclusion, we hope this article has helped you understand better the effectiveness of fogging for mold remediation. While fogging can be a useful tool in the mold remediation process, it’s important to recognize that it’s not a standalone solution.
How effective is fogging for mold remediation tells its proper application as part of a comprehensive approach. When used in conjunction with thorough cleaning, moisture control, and addressing the root cause of mold growth, fogging can enhance the overall remediation efforts. However, it’s crucial to remember that professional assessment and tailored treatments are often necessary for severe mold issues.
By considering the pros and cons discussed in this article, you’re now better equipped to make informed decisions. This will help you choose the right mold remediation approach for your home or business. Remember, the key to successful mold control is a holistic strategy that combines various methods and preventive measures.